팬텀 파워
팬텀 파워(Phantom Power)는 밸런스드 케이블과 XLR 커넥터를 통해 특정 유형의 마이크 전자 장치에 전원을 공급하는 표준화된 방식입니다. 이 기술은 1966년 Neumann GmbH와 노르웨이 방송국(NRK)이 설정한 48V DC 팬텀 파워 표준에서 유래했으며, 현재는 IEC 61938:2018 표준으로 개정되어 사용되고 있습니다.
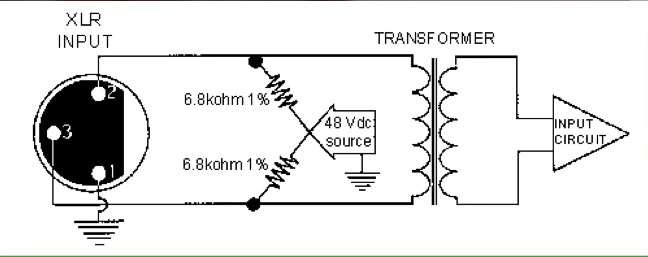
팬텀 파워는 마이크 케이블을 통해 전원을 전달하며, 별도의 전원 케이블이 필요하지 않기 때문에 “팬텀“이라는 이름이 붙었습니다. 일반적으로 +48V DC의 전압을 제공하며, 허용 범위는 ±4V(44~52V)입니다. 높은 전압을 사용하는 이유는 콘덴서 마이크 내부의 캡슐을 빠르게 충전하기 위함입니다.
팬텀 파워의 작동 원리
팬텀 파워는 P48 형식으로 설명되며, 다음과 같은 구조를 가집니다:
- 음극은 케이블 스크린(1번 핀)을 통해 반환됩니다.
이 구성에서 마이크에 공급할 수 있는 최대 전류는 10mA이며, 최대 170mW의 전력을 제공합니다. 대부분의 마이크는 약 4mA 이하의 전류를 사용하지만, 일부 모델은 더 많은 전류가 필요할 수 있습니다. 만약 프리앰프나 오디오 인터페이스가 충분한 전류를 공급하지 못하면, 마이크 성능이 저하될 수 있습니다.
팬텀 파워의 변형
- P12L: 저전력 버전으로, 4mA와 22mW만 제공합니다.
비표준 팬텀 파워
일부 장비는 예산이나 소형화를 이유로 비표준 전압(15V 또는 24V 등)을 사용할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 많은 AKG 마이크는 넓은 범위(9~52V)에서 작동할 수 있지만, 일부 마이크는 낮은 전압에서는 제대로 작동하지 않을 수 있습니다.