선행음 효과
Precedence effect, Hass effect
50ms 이하의 짧은 딜레이는 간격이 매우 짧아서 에코처럼 느껴지지 않는다.
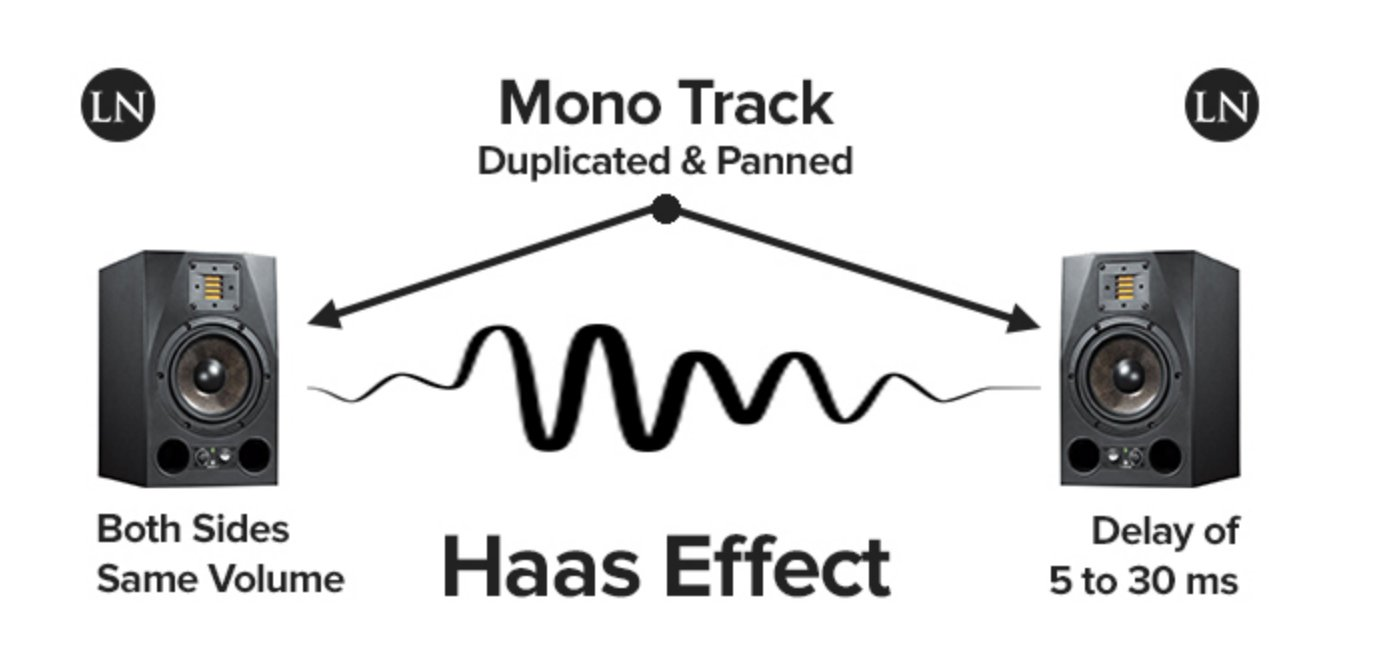
모노의 소리를 스플릿하여 두개로 만든 다음 좌/우로 패닝하고 한쪽 채널에 50ms이하의 딜레이를 주면 소리는 인위적이긴 해도 스테레오로 들리게 된다.1)
선행음 효과를 이용한 딜레이는 다음과 같은 원리로 작동합니다.
딜레이를 활용한 선행음 효과는 다음과 같이 작동합니다:
이를 응용하면, 딜레이를 이용하여 스피커를 통해 소리를 내보낼 때 두 스피커 사이의 시간 차이를 두면 듣는 이들은 그 소리가 더 먼 곳에서 오는 것처럼 들을 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 음향 공간을 조작하거나 사운드의 위치를 조절하여 듣는 이에게 더욱 풍부한 청취 경험을 제공할 수 있습니다.
딜레이를 이용한 선행음 효과는 음향 디자인, 음악 제작, 영화 제작 등 다양한 분야에서 활용되며, 공간적인 감각을 더욱 풍부하게 만드는 데 큰 역할을 합니다.
Precedence effect
Delays of less than 50ms are so brief that they don't create an echo-like effect.
By splitting a mono sound into two and panning them left and right, then applying a delay of less than 50ms to one channel, the sound, while artificially created, becomes perceptible as stereo.
The delay effect using the Precedence effect operates on the following principles:
- Time Delay: Sound travels at the speed of sound. Delay represents the time it takes to transmit a sound signal from one source to another.
- Stereo Listening: Human ears can detect sounds coming from different directions, perceiving the time difference at which two sounds arrive. This allows the brain to determine the directionality and distance of sounds.
The Precedence effect, utilizing delay, functions as follows:
- Centered Sound: Listeners perceiving a sound as coming from the center will feel that the sound reaches their brain directly.
- Lateral Sound: When a sound is heard from one side first, the brain interprets it as if it arrived from that direction. Therefore, the sound will appear to come from that direction.
By applying a delay, one can make listeners perceive the sound as coming from a more distant location between two speakers. This technique is used to manipulate auditory spaces or adjust the position of sounds, providing a richer listening experience to the audience.
The delay-based Precedence effect is applied in various fields, including sound design, music production, and filmmaking, to enhance the perception of spatial dimensions, enriching the overall auditory experience.