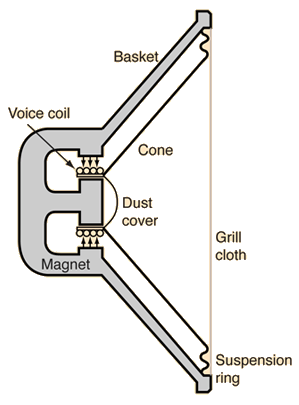
스피커
스피커는 전기 신호를 소리로 변환하는 장치, 즉 트랜스듀서의 한 종류입니다. 이 장치는 다양한 크기와 디자인으로 제작되며, 주로 오디오 신호를 받아들이고 진동을 발생시켜 소리를 생성합니다.
스피커의 주요 구성 요소에는 다음과 같은 것들이 있습니다:
스피커는 오디오 시스템에서 중요한 역할을 하며, 전자기기, 음향 시스템, 차량 오디오 시스템 등 다양한 응용 분야에서 사용됩니다. 전기 신호를 받아들여 음악, 음성 또는 다른 소리를 생생하게 재생하는 데 사용되며, 음질과 성능은 스피커의 디자인과 품질에 따라 다양하게 변화합니다.
Speaker
A speaker is a device that converts electrical signals into audible sound, known as a transducer. It comes in various sizes and designs and is primarily responsible for taking audio signals and generating vibrations to produce sound.
Some of the key components of a speaker include:
- Diaphragm: This is one of the most crucial parts of the speaker and is responsible for vibrating when it receives electrical signals. Typically made of thin plastic or paper, it vibrates to create sound.
- Voice Coil: Wrapped around the diaphragm, the coil receives electrical signals and creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the coil to move the diaphragm and produce sound.
- Magnet: Powerful magnets exist within the speaker and interact with the coil to generate the force that moves the diaphragm.
- Suspension: This component is responsible for centrally positioning the diaphragm. It is a critical part that determines the quality and performance of the speaker.
Speakers play a vital role in audio systems and find applications in various fields, including electronics, audio systems, car audio, and more. They take in electrical signals and reproduce music, voice, or other sounds vividly, with sound quality and performance varying depending on the speaker's design and quality.
Reference
홈레코딩 위키의 스피커 챕터의 모든 내용은 오세진 교수님의 스피커 총론을 기반으로 작성되었음을 밝힙니다.
스피커 총론 - 오세진 저
https://product.kyobobook.co.kr/detail/S000001519043
목차
제 01 장. 소리의 역사
- 1.1. 소리 재생의 시작
- 1.2. 축음기(phonograph)의 발명
- 1.3. 정전형 트랜스듀서(electrostatic transducer)
- 1.4. 라우드스피커(loudspeaker)
제 02 장. 라우드스피커란 무엇인가
- 2.1. 라우드스피커란 무엇인가?
제 03 장. 스피커 분류
- 3.1. 구동방식에 따른 분류
- 3.2. 스피커 영구자석의 형태에 따른 분류
- 3.3. 구조 및 형상에 따른 분류
제 04 장. 스피커 부품
- 5.1. 평면파(plane wave)와 구면파(spherical wave)
- 5.2. 횡파(transverse wave)와 종파(longitudinal wave)
- 5.4. 파수(wave number, k)와 각진동수(angular frequency, Ω)
- 5.5. 음압(sound pressure, p)
- 5.7. 음의 세기(sound intensity, Iac)와 파워(power, W)
- 5.8. 음속(sound velocity, c)
- 5.9. 입자속도(particle velocity, u)
- 5.11. 임피던스(impedance, Z)
- 5.13. 스펙트럼(spectrum)
- 5.14. 지향특성(directivity)
- 5.15. 주파수특성(frequency response)
제 06 장. 스피커 특성
- 6.1. 주파수 특성
- 6.2. 효율(efficiency)
- 6.3. 지향특성(directivity)
- 6.4. 전기임피던스 특성
- 6.5. 위상특성(phase property)
- 6.6. 과도특성(transient response)
- 6.7. 왜곡(distortion)
- 6.8. 최대변위(maximum displacement)
- 6.9. 감도(sensitivity)
- 6.10. 진동계의 운동특성
- 6.12. 열(파워) 압축(thermal 또는 power compression)
- 6.13. 열적 시간상수(thermal time constant, duration effect)
- 6.14. 냉각작용
- 6.15. 파워 핸들링(power handling)
- 7.1. 방사 임피던스
- 7.2. 스피커의 공기질량
- 7.3. 진동계의 유효질량
- 7.4. 스피커의 컴플라이언스
- 7.5. 구동세기(Bℓ) 측정
- 7.6. 보이스 코일의 질량
- 7.7. 보이스 코일의 인덕턴스 계산
- 7.9. 전체저항의 계산
- 7.10. 스피커 극성결정
- 7.11. 진동판의 가속도 계산
- 7.12. 진동판의 최대변위
제 08 장. 등가회로 해석법
제 09 장. 라우드스피커의 전기역학적 해석
- 9.1. 기계적 해석
- 9.2. 공기의 영향
- 9.4. 테브닌의 등가회로(Thevenin equivalent circuit)
제 10 장. 돔 스피커
- 10.1. 중심축에서 음압특성
- 10.2. 지향특성
- 10.3. 음압분포 및 에너지 흐름
- 10.4. 링 소스(ring source)의 주파수특성
- 10.5. 링 소스(ring source)의 에너지 흐름
제 11 장. 혼 스피커
제 13 장. 크로스오버
제 14 장. 스피커시스템
- 14.1. 배플(Baffle)
- 14.2. 무한배플에서 인클로저까지
- 14.3. 인클로저
- 14.4. 인클로저의 재료특성
- 14.5. 흡음재
- 14.6. 보강재
- 14.7. 정재파
- 14.8. 종류에 따른 특징
제 15 장. 틸-스몰(Thiele-Small) 파라미터
[공지]회원 가입 방법
[공지]글 작성 및 수정 방법